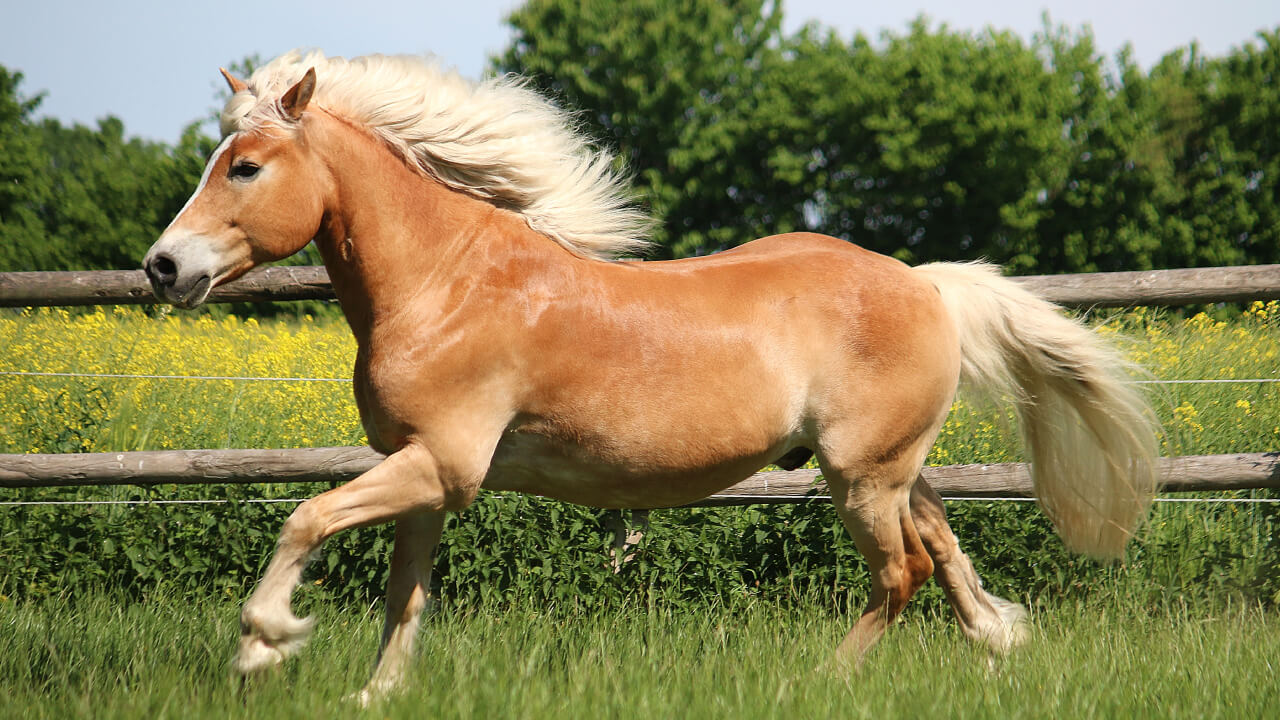
When looking at a horse’s profile, you might notice unfamiliar terms like bay or chestnut. Since these terms are followed by ‘coat,’ it’s easy to guess they refer to the horse’s hair or fur. However, many such terms like ‘roan’ or ‘grey’ don’t immediately evoke an image of what the horse looks like.
In reality, words like ‘roan’ and ‘grey’ can be confusing for those unfamiliar with horses. This article explains what horse coat colors and manes refer to, and explores the different types and names used for them.
Expressing Horse Hair
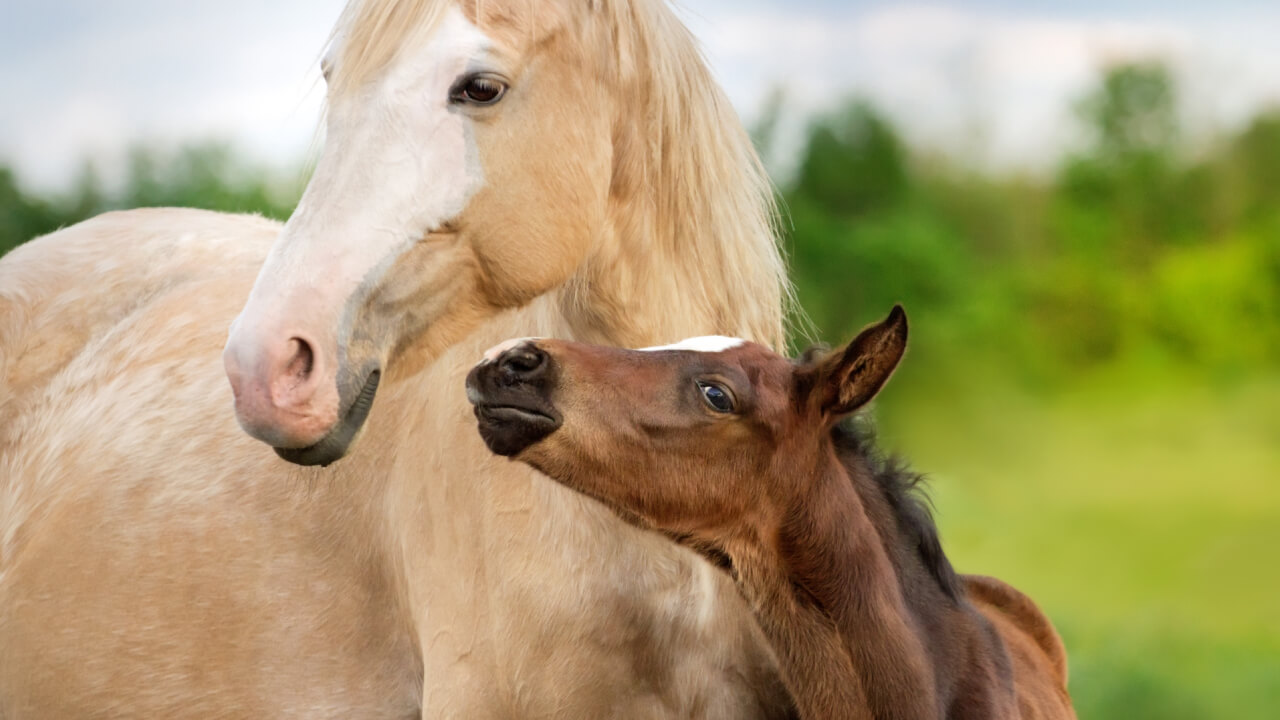

Horses come in various colors such as black, white, and brown. When researching horse hair, the terms ‘mane’ and ‘coat’ are commonly used. ‘Mane’ usually conjures images of soft, shiny hair, but in the context of horses, ‘mane’ and ‘coat’ are often used interchangeably, referring to the overall hair covering.
Horse hair is categorized into two types: the coat covering the body and the longer hair such as the mane, tail, and forelock. The coat hair changes with the seasons, from summer to winter, serving as protection for the horse.
Types and Names of Coat Colors
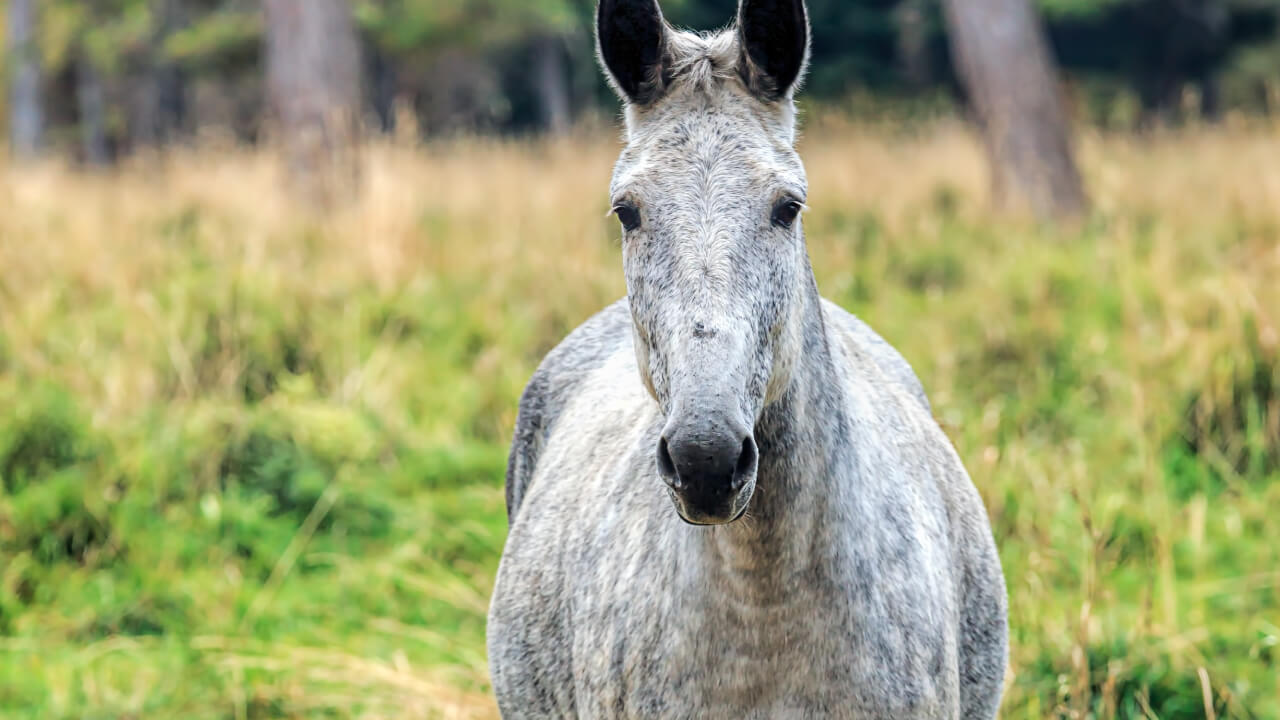

Just like humans, horses vary in facial features, hair color, and size. Many people identify horses by these details, especially their hair color, which is easy to observe since it covers their entire body.
Horse hair covers the entire body, making it a useful identification feature. However, horse coat colors are not simply classified as ‘brown’ or ‘black.’ The same general color can have different names depending on the specific shade or pattern. So, what are the main types of horse coat colors? Here is an overview of the major categories and their names.
What Are Horse Coat Colors?
Horse coat colors are not just based on the visible color of the hair. They are classified by the body hair, skin color, and patterns, which all help in individual identification. The presence of melanin pigment in the hair determines the color, with different amounts resulting in different shades.
Types of Coat Colors
There are over 100 hues when considering all detailed variations. The main categories are ‘bay,’ ‘black bay,’ ‘blue roan,’ ‘black,’ ‘chestnut,’ ‘sorrel,’ ‘grey,’ ‘dapple grey,’ ‘pale grey,’ ‘white,’ ‘pied,’ ‘flea-bitten,’ ‘slate,’ and ‘pashmina.’
Among these, the Japan Stud Book International officially recognizes eight as typical Thoroughbred coat colors: bay, black bay, blue roan, black, chestnut, sorrel, grey, and white.
Names and Features of Main Coat Colors
Here are descriptions of the 14 main horse coat colors:
- Bay: Ranges from light reddish-brown to dark brown; the mane and lower legs are black. Famous example: Deep Impact.
- Black Bay: Dark reddish-brown body with black mane and lower legs. Some are almost black, with darker brown around the eyes, belly, or inside. Example: Narita Brian.
- Blue Bay: Almost entirely black with slight brown highlights on the nose, eyes, or flank. Example: Mejiro Ramonu.
- Black: Black hair and mane, with seasonal shades sometimes appearing. Example: Sea The Stars.
- Chestnut: Reddish-yellow body with darker brown or white long hair. Example: Yamanotop Gun.
- Sorrel: Bright brown to dark brown body with darker or white mane and tail. Example: Sakura Laurel.
- Grey: Derives from chestnut, roan, or blue roan, with white mixed in, becoming pure white with age. Example: Tamamo Cross.
- White: Entire body is white, with neural white hair. The reason for this is unknown. Sometimes skin spots are visible. Example: Yuki-chan.
- Pied: Pink skin with ivory-colored hair; seen in Hokkaido native breeds. Example: Rare occurrence.
- Flea-Bitten: Light yellow-brown to flaxen coat with black mane and lower legs. Common in Hokkaido breeds.
- Moon Coat: Cream-colored with cream or white long hair. Found in Hokkaido native horses and American Palominos.
- Faded: Similar to pied but with limited white hair in specific areas; does not change with age. Example: Not specified.
- Piebald: White spots pattern across the body, with color variations named ‘chestnut’ or ‘blue,’ combined with ‘pied’ or ‘pinto’ terminology.
Horses’ Grooming and Hair Care
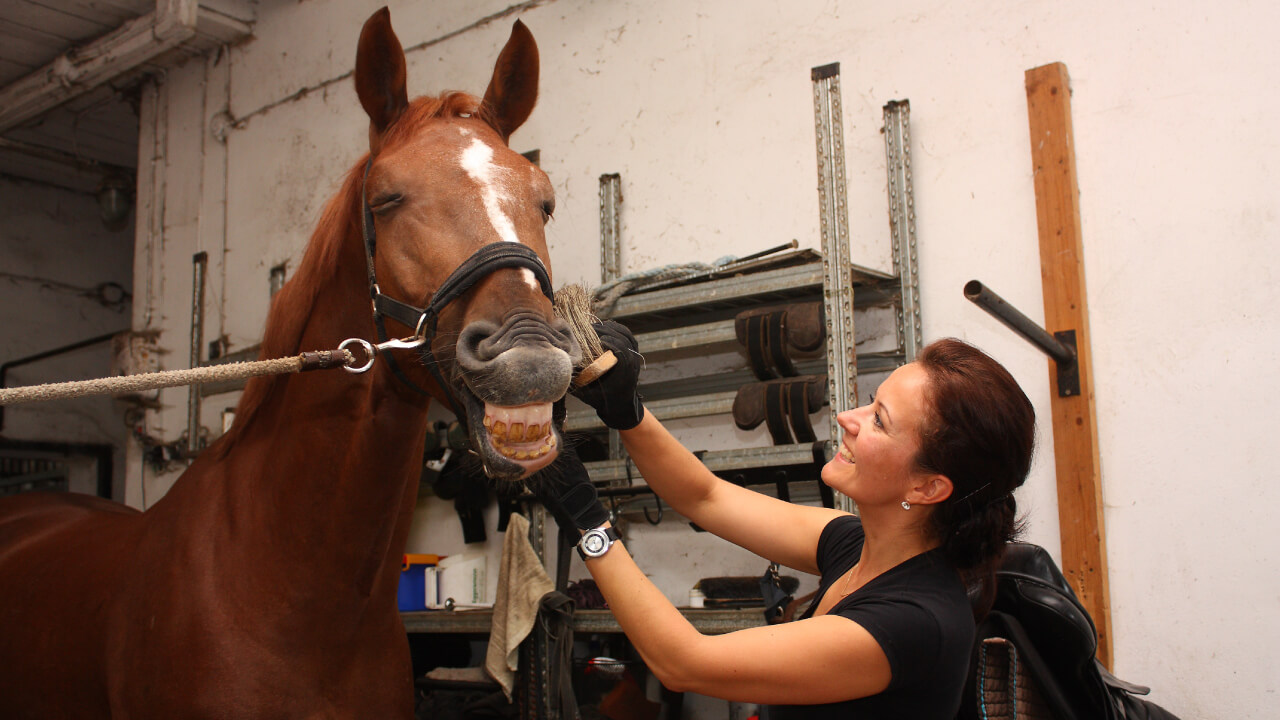

Once familiar with the different horse coat colors, you might become curious about the horses around you. Since surface hair, longer hair, and even skin spots can be tricky to identify at a glance, careful observation is necessary.
Regular grooming, such as brushing, helps in observing and maintaining the horse’s coat. Here is a guide to brushing techniques.
Tools for Grooming
Did you know there are different types of brushes for grooming? The type of brush chosen depends on its purpose.
For example, a plastic brush is used to remove mud splashes during riding or water cleaning.
A rubber brush massages from the base of the hair, removing dandruff and dirt.
A root brush removes large debris or loosened hair from the surface.
A soft hair brush smooths the coat and removes dust or tiny particles.
Grooming Tips
Keeping a horse clean helps prevent skin diseases. Even short on time, brushing and lightly removing dirt with a root or soft brush can be beneficial, especially before or after lessons.
On rainy days, wipe the horse down to prevent body heat loss. Since hair grows from the back toward the belly, rainwater generally flows downward, helping maintain temperature.
When brushing, follow the hair’s natural flow from top to bottom, applying a firm but gentle pressure for better dirt removal. Be careful to avoid areas the horse prefers not to be touched.
Summary
In conclusion, even colors that look the same—like black or white—can differ significantly upon closer inspection, as horse coat colors have much depth. Next time you see a horse at a lesson or on TV, try to identify its coat color. Observing and understanding horses’ coat colors enhances your connection and enjoyment of riding and caring for horses.